The cloud revolution promised flexibility and cost efficiency, but for many organizations, AWS bills have become a source of anxiety rather than empowerment. Stories of startups facing five-figure surprise invoices or enterprises discovering rogue resources racking up charges are all too common. Understanding how to control and predict your AWS spending is no longer optional; it’s essential for business survival.
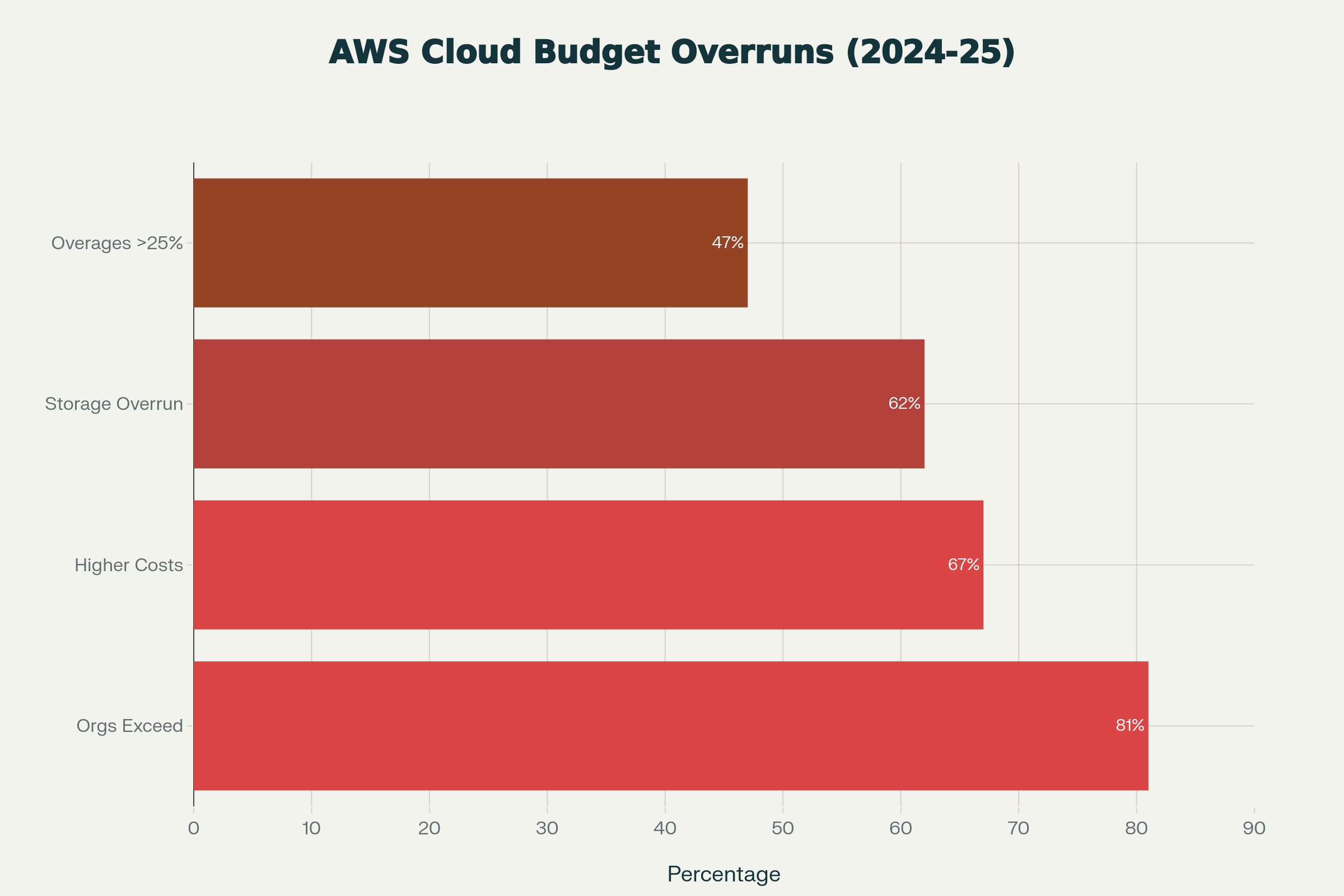
The cloud computing revolution promised organizations flexibility and cost efficiency, but for many enterprises, AWS bills have become a source of financial anxiety rather than empowerment. Industry reports reveal a troubling reality: 81% of organizations exceed their cloud budgets, with 47% reporting overages exceeding 25% of their planned spending. Enterprise teams regularly face five-figure surprise invoices, while startups discover rogue resources racking up thousands in charges. More disturbingly, research shows 27% of cloud spending is pure waste, climbing to 55% in organizations lacking formal optimization strategies. Understanding how to control and predict AWS spending is no longer optional—it’s essential for business survival.
The Hidden Nature of Cloud Costs
Amazon Web Services operates on a pay-as-you-go model that offers tremendous flexibility, but this same flexibility can become a financial liability. Unlike traditional infrastructure with predictable monthly costs, cloud spending can spiral unexpectedly due to a combination of complex pricing models, resource sprawl, and automatic scaling behaviors.
For many organizations, this uncertainty manifests in concrete financial pain. A 2024 Flexera State of the Cloud Report found that organizations exceed budgets by an average of 15%, but this masks even more troubling patterns: 84% of organizations now consider managing cloud spend their top IT challenge, and 67% of global organizations report experiencing higher-than-expected cloud costs compared to their initial projections. Additionally, 62% of enterprises experienced cloud storage cost overruns in 2024, representing a nine percentage point increase from the previous year. The scale of enterprise spending is staggering: 31% of organizations now spend more than $12 million annually on public cloud alone, with some exceeding $1 billion per year.
Common Culprits Behind AWS Cost Overruns
Data Transfer Fees: The Silent Budget Killer
One of the most overlooked aspects of AWS pricing is data transfer costs. While data ingress (uploading to AWS) is typically free, egress charges for moving data out of AWS or between regions can accumulate rapidly and unexpectedly. AWS charges $0.09 per GB for the first 10 TB transferred out to the internet, decreasing to $0.06 per GB for transfers exceeding 150 TB monthly. Cross-region transfers cost $0.01–$0.02 per GB depending on region combinations, while cross-availability zone transfers within the same region add $0.01 per GB in each direction.
In a documented case study, one enterprise discovered that data transfer charges alone accounted for 45% of their “EC2 Other” costs, totaling $54,000 annually, money spent on charges they didn’t know existed until conducting a comprehensive audit. Data transfer costs are so pervasive that they represent one of the top five unexpected AWS charges organizations encounter.

For AI and machine learning teams, data transfer costs become particularly acute. Machine learning teams downloading large training datasets repeatedly, applications serving media files to global users, or routine backups to external systems can generate thousands of dollars in unexpected transfer fees. Cross-region data transfers are particularly expensive: transferring 1 TB between regions like US East (North Virginia) and Asia Pacific (Mumbai) costs $20,480 in egress fees alone for a petabyte of data.
Idle and Forgotten Resources
The ephemeral nature of cloud infrastructure makes it deceptively easy to spin up resources and forget about them. Development environments meant to be temporary, test instances that outlived their purpose, old snapshots and AMIs gathering digital dust—these “zombie resources” continue generating charges long after they’ve ceased being useful.
A comprehensive audit often reveals shocking waste:
-
Unused Elastic IPs: These cost $3.60 per month when unattached to running instances
-
Unattached EBS volumes: Common storage remnants costing $0.05–$0.10 per GB-month
-
Aged snapshots and AMIs: Legacy backup copies accumulating at $0.05 per GB-month
-
EC2 instances left running over weekends and holidays: Development environments running 24/7 despite being used only during business hours

In one documented case, EC2 “other” costs the collection of miscellaneous charges reached $120,000 annually, representing 20% of total EC2 expenses. The breakdown revealed: data transfer (45% or $54,000), EBS snapshots (30% or $36,000), Elastic IP addresses (15% or $18,000), and other miscellaneous charges (10% or $12,000).
Auto-Scaling Gone Wrong
Auto-scaling is designed to optimize costs by adjusting resources based on demand, but misconfigured scaling policies can have the opposite effect. An overly sensitive scale-out policy might spawn dozens of instances in response to a temporary traffic spike. In extreme cases, runaway processes have triggered continuous scaling that drained entire budgets in hours.
One gaming company experienced a dramatic example: a poorly configured auto-scaling policy during peak traffic times resulted in $1 million in charges before the issue was discovered and corrected. Without proper guardrails, monitoring thresholds, and manual kill switches, auto-scaling transforms from a cost optimization tool into an automated path to budget disaster.
Reserved Instance Mismanagement
Reserved Instances offer significant discounts up to 72% compared to on-demand pricing but require accurate capacity planning. Organizations that over-commit to reserved capacity find themselves paying for unused resources for months or years. Conversely, those who under-commit miss out on savings and pay premium on-demand rates.
The situation becomes more complex with different RI types, payment options, and the challenge of predicting future needs in rapidly evolving environments. Many organizations purchase Reserved Instances based on peak capacity requirements, then face utilization rates of 40–60%, effectively wasting 40–60% of their RI investment.
Development and Testing Sprawl
Development teams need flexibility to innovate, but this often leads to uncontrolled proliferation of resources. Each developer might spin up their own environment, QA teams create multiple test configurations, and CI/CD pipelines generate temporary resources. Without governance, these environments multiply unchecked.
Research shows that 30% of EC2 instances in typical organizations are significantly oversized for their actual workloads. When multiplied across entire development teams, this inefficiency accumulates into six-figure annual waste. One organization discovered that their development environments were running at only 32% utilization while sized for peak capacity.
Strategies to Control AWS Spending
Implement Comprehensive Tagging and Organization
The foundation of cost control is visibility. Implement a mandatory tagging strategy that identifies resource owners, projects, environments, and cost centers. AWS Organizations and Service Control Policies can enforce tagging requirements, while Cost Allocation Tags enable detailed cost breakdowns. Tags should include creation dates, intended lifespan, and responsible teams to facilitate accountability and cleanup efforts.
Set Up Cost Monitoring and Alerts
AWS Cost Explorer, CloudWatch, and AWS Budgets provide tools to track spending patterns and set alerts. Create budgets at multiple levels: organizational, account, project, and service-specific. Configure alerts at thresholds like 50%, 75%, and 90% of budget to enable proactive intervention before costs spiral. Enable AWS Cost Anomaly Detection to identify unusual spending patterns that might indicate misconfigurations or security breaches.
Rightsize Your Infrastructure
Many organizations over-provision resources based on peak capacity or worst-case scenarios. AWS Compute Optimizer and Trusted Advisor provide rightsizing recommendations based on actual utilization patterns. Regularly review these recommendations and adjust instance types, downsize over-provisioned databases, and eliminate unnecessary redundancy. Remember that rightsizing is an ongoing process, not a one-time exercise, as workload patterns evolve.
Implement Lifecycle Policies and Automation
Automate the cleanup of resources that should be temporary. Use AWS Lambda functions triggered by CloudWatch Events to shut down development instances outside business hours, delete old snapshots, and terminate instances tagged as temporary after their expiration date. S3 lifecycle policies can automatically transition data to cheaper storage tiers or delete it after specified periods. Infrastructure as Code tools like Terraform can include automatic resource expiration as part of deployment workflows.
Optimize Data Transfer Patterns
Minimize cross-region and cross-AZ data transfers by carefully planning architecture. Use CloudFront CDN to reduce egress costs for frequently accessed content, configure S3 Transfer Acceleration judiciously, and consider VPC endpoints for AWS service communication to avoid internet gateway charges. For large dataset operations, evaluate whether processing should happen closer to where data resides rather than moving data to compute resources.
Establish Governance and Access Controls
Implement least-privilege IAM policies that restrict who can launch expensive resources. Use Service Control Policies in AWS Organizations to prevent certain instance types or regions from being used without approval. Require approval workflows for launching large instances or creating reserved capacity. Make cost visibility part of your team culture by sharing regular cost reports and recognizing teams that optimize effectively.
Leverage Spot Instances and Savings Plans
For workloads that can tolerate interruptions, Spot Instances offer discounts up to 90% compared to on-demand pricing. Modern containerized applications and batch processing jobs are excellent candidates for Spot. Savings Plans provide flexibility similar to Reserved Instances but with broader applicability across instance families and services, making them easier to utilize fully as your infrastructure evolves.
The Spheron AI Alternative: Rethinking GPU Infrastructure Costs
While these strategies can help control AWS costs for general workloads, organizations running AI and machine learning workloads face a particularly acute challenge. GPU compute on AWS is expensive, and the cost optimization strategies above offer limited relief when you’re training large models or running inference at scale. This is where reconsidering your infrastructure provider becomes strategic.
The GPU Cost Problem on Traditional Clouds
Running AI workloads on AWS typically means using EC2 P4 or P5 instances with NVIDIA GPUs. An A100 GPU on AWS can cost approximately $3.30 per hour or more, and training state-of-the-art models often requires multiple GPUs running for extended periods. For a startup or research team, these costs can consume the majority of available budget, leaving little room for experimentation or rapid iteration. Even with Reserved Instances or Savings Plans, the baseline cost remains prohibitively high for many use cases.
Traditional cloud providers also impose data transfer fees that particularly impact AI workloads. Moving large datasets in and out for training, transferring model checkpoints between regions, or serving inference results to global users all generate additional charges that compound the already high compute costs.
Spheron AI: Purpose-Built for Cost-Effective AI Infrastructure
Spheron AI represents a fundamentally different approach to GPU infrastructure that addresses the core cost challenges facing AI teams. As an aggregated GPU cloud platform, Spheron unifies capacity from multiple GPU providers worldwide into a single unified dashboard, creating a marketplace that drives costs down through competition and efficient utilization of underutilized hardware.
The platform delivers up to 60-75% cost savings compared to traditional cloud providers. That same A100 GPU that costs around $3.30 per hour on AWS runs for approximately $1.50 per hour on Spheron, a 65% reduction that can mean the difference between an affordable training run and a budget-breaking one. Even compared to specialized GPU providers, Spheron maintains a cost advantage with rates that are 37% cheaper than Lambda Labs, 44% cheaper than GPU Mart, and competitive with or better than Vast.ai‘s marketplace.
Full Control Without the Cloud Tax
Beyond raw cost savings, Spheron provides full VM access with root control, eliminating the restrictions that containerized cloud services impose. Your team gets complete control over OS configurations, driver installations, and system-level optimizations, crucial for complex AI pipelines requiring custom libraries or specific GPU kernel tweaks. This is the level of control you’d have with bare metal infrastructure but delivered with cloud convenience.
The platform’s bare-metal architecture runs directly on GPU servers without virtualization overhead, eliminating the hypervisor latency and “noisy neighbor” interference common in traditional cloud VMs. Your models get 100% of the hardware’s capabilities with consistent peak throughput, translating to 15-20% faster compute performance and up to 35% higher network throughput for multi-node jobs. When you’re paying for compute time, faster execution directly reduces costs further.
No Hidden Fees or Data Transfer Charges
One of Spheron’s most compelling advantages is the elimination of the data transfer fees that plague AWS users. There are no ingress or egress charges and no bandwidth fees. A built-in CDN accelerates data access globally without additional cost. For AI teams regularly moving large datasets, this alone can save thousands of dollars monthly and makes cost forecasting dramatically simpler.
Pay-as-you-go pricing with per-second billing means you pay only for what you actually use, with no hidden fees or surprise charges. This transparency stands in stark contrast to the complex, multi-layered pricing models of traditional clouds where costs can emerge from unexpected sources.
Enterprise-Grade Hardware Options
Spheron supports a comprehensive range of hardware from cutting-edge NVIDIA HGX systems with SXM5 GPUs, NVLink/NVSwitch, and InfiniBand interconnects for large-scale multi-node training down to standard PCIe-based GPUs for development and testing. This flexibility allows you to select precisely the right hardware for each workload, using high-performance SXM5 H100 clusters with InfiniBand when you need maximum throughput, then scaling down to affordable single PCIe GPUs for lighter tasks.
The platform currently spans over 2,000 GPUs across 150+ global regions, providing access to a diverse inventory that includes the latest RTX 4090s, A6000s, A100s, and H100s with no waiting periods. Whether you need one GPU or a cluster of hundreds, the capacity scales to your requirements.
Resilience and Reliability
Spheron’s aggregated network architecture inherently provides resilience that single-datacenter clouds cannot match. The distributed network of GPUs across many regions means there’s no single point of failure. If one node or provider experiences issues, workloads can seamlessly shift to another. This redundancy enables production AI deployments with confidence while simultaneously avoiding vendor lock-in that might trap you in an expensive ecosystem.
Seamless Integration and Developer Experience
Despite the infrastructure complexity behind the scenes, Spheron abstracts away operational headaches. The platform integrates with existing workflows through Terraform providers, SDKs, and APIs. Real-time metrics dashboards, health checks, and auto-scaling groups simplify ML operations without requiring extensive DevOps expertise. Your team can deploy containers or models and spin up secure GPU instances in minutes, staying focused on model development rather than infrastructure management.
Making the Strategic Decision
Avoiding unexpected AWS costs requires a combination of disciplined practices, automated controls, and strategic architecture decisions. For general workloads, implementing the cost management strategies outlined above can significantly reduce waste and improve predictability. However, for AI and machine learning workloads where GPU compute dominates spending, these optimizations may not be sufficient.
Organizations should evaluate whether their AI infrastructure truly needs to run on traditional cloud providers or whether purpose-built alternatives like Spheron AI can deliver superior economics. The 60-75% cost savings, elimination of data transfer fees, bare-metal performance advantages, and transparent pricing model can fundamentally change the economics of AI development and deployment.
The question isn’t just about avoiding unexpected costs; it’s about choosing infrastructure that aligns with your actual needs rather than accepting the limitations and pricing structures of legacy cloud providers. For AI-driven organizations, that strategic choice can free up substantial budget for innovation, enable more experimentation, and ultimately accelerate your competitive position in an increasingly AI-driven world.
Every dollar saved on infrastructure is a dollar you can reinvest in the models, talent, and innovation that actually differentiate your business.
